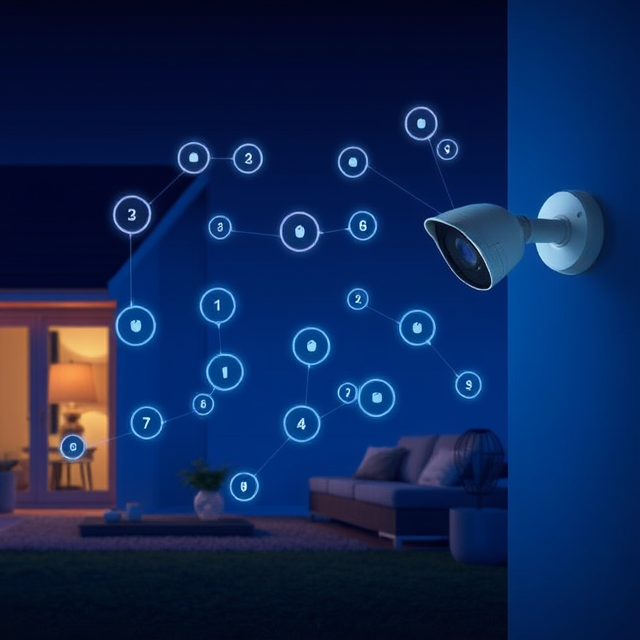
In today's world, security is more important than ever. Preventing intrusions, theft, attacks, fire hazards, and medical emergencies (Personal Emergency Response Systems or PERS) is a growing challenge. Constant surveillance and monitoring are required to ensure safety 24/7.
Tackling these security concerns can be easily achieved through an IoT-based smart home security system, which is designed to meet modern security needs.
Let’s explore how an IoT smart home security ecosystem helps keep our homes and businesses safe.

5-Step End-to-End Solution and the Essential Components
Addressing security concerns requires following key steps:
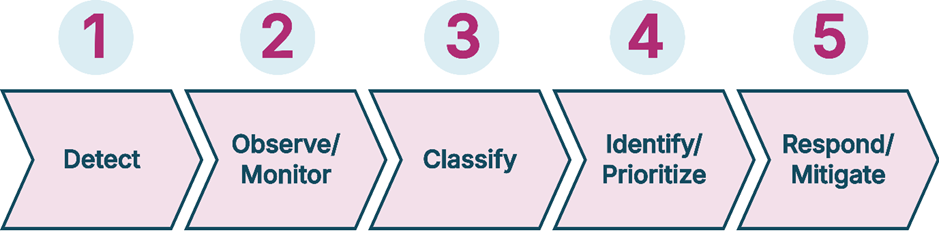
1. Detect
Detection is the first step in identifying a potential threat. IoT smart home security systems use a range of sensors and detectors (e.g., motion detectors, door/window contact sensors, smoke detectors) to immediately recognize any unusual activity or hazards. Detection is crucial to alert the system about potential risks, whether it’s an intrusion, fire, or gas leak.
2. Observe/Monitor
Once a threat is detected, the system enters the monitoring phase, where cameras, sensors, and apps provide real-time surveillance. Monitoring helps verify the situation and distinguish between genuine threats and false alarms. For example, cameras can confirm if a movement was caused by a person or a pet, reducing the chances of unnecessary responses.
3. Classify Alarms
Classifying alarms is about assessing the nature of the detected issue. In this phase, the Alarm Monitoring Service (AMS) plays a crucial role. AMS helps categorize alarms into different types, such as:
- False Alarms: Pet movements, weather conditions, or minor disturbances that don’t require intervention.
- Critical Alarms: Intrusions, fires, gas leaks, or medical emergencies that need immediate attention.
AMS ensures that the classification is done correctly, preventing false alarms from triggering unnecessary responses, while ensuring that genuine threats are quickly identified.
4. Identify/Prioritize Alarms
After classifying the alarms, the system must identify and prioritize them. The AMS further helps in this process by prioritizing alarms based on urgency and severity. For instance:
- Intrusion Alarms: Can be prioritized for immediate action if an entry is detected after hours.
- Fire Alarms: These should take precedence as they involve potential life-threatening situations.
AMS supports in assessing the level of risk and deciding which alarms need to be addressed first, ensuring timely responses.
5. Respond/Mitigate
Finally, the response phase involves taking appropriate action based on the priority and type of alarm. This could include notifying security personnel, activating alarms, or sending alerts to emergency services. For example, if a fire is detected, the system might automatically trigger sprinklers, alert the fire department, and notify homeowners.
These five steps form the core of any smart home security system, ensuring rapid, efficient responses to various threats and emergencies.
Key Requirements for a Smart Home Security Ecosystem
An effective smart home security system integrates hardware, software, essential features, and utility tools, with the option to retrofit legacy systems. It also includes the ability to outsource Central Monitoring Services (CMS) and response teams, ensuring a comprehensive and tailored security solution.
Hardware
The essential hardware in an IoT-based smart home security system includes a variety of devices that work together to ensure seamless protection. These devices typically include:
- Intrusion Detection Sensors: Motion detectors (PIR, microwave), door/window contact sensors, glass-break sensors.
- Fire and Gas Detectors: Smoke alarms, heat detectors, carbon monoxide detectors.
- Surveillance Devices: Cameras, photo verification devices, video doorbells.
- Smart Home Devices: Lights, locks, thermostats, etc., that can be integrated for automation and enhanced security.
Additionally, more advanced outdoor protection devices may be included for areas that are vulnerable to break-ins or accidents.
Software
A proper communication protocol is critical for seamless operation of the smart home security system. This protocol must support long-distance communication and provide secure, reliable connectivity. Popular communication methods include:

- Dedicated Operating Systems (OS): An OS built specifically for security devices can offer better control and support for managing various smart home devices.
- GSM, Ethernet, and Wi-Fi: These ensure constant, uninterrupted communication between devices.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Cloud-based systems offer remote access to security settings and device configurations.
Features
An advanced smart home security system offers a variety of features to enhance performance and usability:
- Pet-Friendly: Devices designed to reduce false alarms caused by pets moving within the house.
- Long Battery Life: Devices that last longer and ensure continuous protection.
- User-Friendly Apps: Both mobile and desktop apps with simplified, single-interface control.
- 24/7 Protection with Backup: Protection continues even during power outages, with up to 50 hours of battery backup.
- Scalability: The system can be easily scaled to accommodate additional devices or larger premises.

The Need for Retrofitting Legacy Systems and Overcoming Challenges
Many homes and businesses already have basic security devices, such as cameras, sensors, and alarms. However, these systems are often outdated or managed manually, which can be time-consuming and inefficient. This is where retrofitting comes in—upgrading legacy systems by adding an Alarm Management Service (AMS) device that integrates older security systems with modern IoT technology.

This process allows users to continue using their existing devices while benefiting from the latest in IoT features, making security management easier and more efficient. Retrofitting not only saves the cost of replacing the entire security system but also brings older systems up to date, ensuring they are compatible with newer technologies
While retrofitting offers a great solution, there are common challenges in implementing IoT-based smart home security systems, especially for those upgrading legacy setups. These include:
Challenges:
- Old Devices: Legacy devices such as reed switches, PIR sensors, and fire detectors may no longer meet current standards, reducing their effectiveness.
- Communication Issues: The shutdown of older communication networks like 2G/3G can hinder connectivity with newer devices and cloud services.
- Wired System Upgrades: Some older systems may require complete rewiring to accommodate new IoT components, which can be costly and disruptive.
- Outdated Interfaces: Legacy systems often feature complex or difficult-to-use controls that do not provide the user-friendly experience offered by modern IoT systems.
Solutions:
- New Life for Old Devices: By integrating IoT solutions into existing security systems, outdated devices can still be utilized, avoiding the need for full replacements.
- Cost-Effective & Eco-Friendly: Our modules allow you to connect third-party wired or wireless devices to modern hubs, offering an affordable and environmentally friendly solution.
- Wide Compatibility: These modules support over 100 different detectors, including IR sensors, gas detectors, thermostats, and keypads, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of legacy devices.
- Mobile/Cloud Control: With mobile apps and cloud-based management, users can control their systems from anywhere, making security monitoring more convenient and streamlined.
By retrofitting older systems with AMS devices and modules, businesses and homeowners can enjoy the benefits of IoT smart home security without the need for a complete overhaul of their existing infrastructure. This approach provides flexibility, cost-efficiency, and enhanced compatibility with a wide variety of sensors and devices.
Utility Tools
To ensure seamless integration and maintenance of a smart home security system, several utility tools are available:
- Device Compatibility Checker: Ensures new devices are compatible with the existing setup.
- Battery Life Calculator: Estimates how long a device will operate before needing a recharge.
- Video Storage Calculator: Helps calculate the required storage for video surveillance footage.
- Radio Communication Range Calculator: Determines the effective range for radio-based communication.
- Data Usage Calculator: Estimates the data consumption of connected devices, helping avoid network overload, especially for cloud storage or streaming.
- Signal Strength Analyzer: Assesses wireless signal strength to ensure optimal device placement and avoid network dead zones.
- Network Bandwidth Calculator: Calculates the bandwidth needed to support all devices, ensuring smooth communication and real-time surveillance.
- Cost Savings Estimator: Estimates savings from energy-efficient devices or system optimization to justify IoT investment.

Additional: Central Monitoring Service (CMS) and Response Teams

For comprehensive security, some users may opt for outsourced CMS (Central Monitoring Service) and response teams. These services monitor alarms round the clock and ensure a swift, professional response in case of an emergency. They can assist in handling various security situations efficiently, reducing the burden on homeowners.
Impact of IoT Security Systems
An IoT-based smart home security system simplifies handling various security concerns using the 5-step process, integrating hardware, software, and utility tools for effective, responsive protection. It also leverages the ability to retrofit legacy systems, ensuring compatibility with older devices. Additionally, the option to outsource Central Monitoring Services (CMS) and response teams provides enhanced security management. Here's how these components work in action across different types of security events.
| Security Type | Detect | Observe/Monitor | Classify | Identify/ Prioritize |
Respond/ Mitigate |
| Intrusion Detection | PIR sensors, door/window sensors | Cameras, photo verification | False alarm or genuine threat | High priority for intrusion | Notify homeowner, trigger alarm |
| Fire Protection | Smoke, heat detectors | Cameras, monitoring systems | False alarm or real threat | Prioritize fire emergency | Activate sprinklers, alert fire department |
| Medical Emergencies | Fall detectors, medical alarms | Cameras, monitoring systems | Determine severity of emergency | Prioritize medical emergency | Alert medical teams, notify family |
| 24/7 Monitoring | Continuous monitoring | Cameras, motion sensors | False alarm or real threat | Prioritize based on severity | Notify security team, trigger alert |
This table reflects the process and how IoT security components—hardware (e.g., sensors, cameras), software (e.g., cloud infrastructure, mobile apps), features (e.g., long battery life, user-friendly apps), and utility tools (e.g., device compatibility checker, signal strength analyzer)—work together at each stage. Retrofitting legacy systems with AMS devices allows older devices to integrate smoothly with newer IoT technology, while outsourcing CMS and response teams provides round-the-clock support for swift mitigation.
By following this 5-step solution, you can efficiently address a wide range of security concerns, enhance the effectiveness of your system, and ensure a comprehensive, tailored security solution for any environment.
Conclusion
Homes of the past were vulnerable to security issues and tackling them was often left to individuals. While security devices like cameras have made security more manageable, they still require constant monitoring and aren’t proactive in handling threats. IoT devices, however, are proactive and handle security automatically.
In this blog, we explored how a Central Monitoring Service (CMS) and Alarm Monitoring Service (AMS) work together to enhance home security. Future blogs will dive deeper into these services for a more detailed understanding.
Finally, smart homes are not just homes with smart devices—they are homes that are always safe. Ensuring security through IoT devices makes homes safer and smarter, combining automation, monitoring, and rapid response capabilities.

