What is HFM?
Hyperion Financial Management (HFM) is an advanced financial consolidation and reporting tool from Oracle. It enables enterprises to manage and streamline their financial close and reporting processes. HFM is part of the Oracle Hyperion suite, designed to provide a centralized platform for consolidating financial data, applying currency translations, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
HFM’s strength lies in its ability to handle complex corporate hierarchies, perform intercompany reconciliations, and generate dynamic financial reports. Businesses use HFM to gain accurate, timely insights into their financial performance while maintaining compliance with global financial regulations such as IFRS and GAAP.
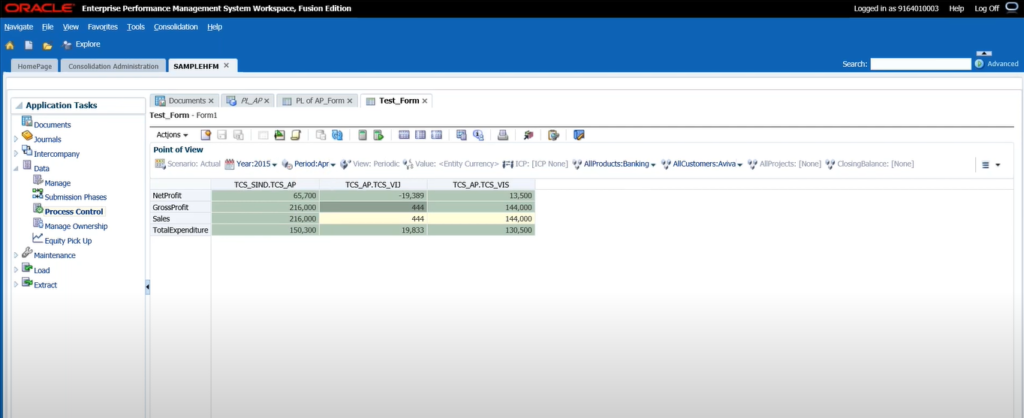
Hyperion Dashboard'
Key Concepts in HFM
1. Data Forms and Grids
Data forms and grids are fundamental components of HFM that facilitate data entry and analysis.
- Data Forms: These are customizable interfaces where users can input financial data. Forms are ideal for structured data entry tasks and can be customized with different row/column settings, fonts, and color schemes. They provide dropdowns for POV (Point of View) selection, helping users filter the data they need.
- Grids: Grids are used for viewing and analyzing data but are less customizable compared to forms. They are more suitable for backend data exploration and structured reporting.
2. Dimensions
Dimensions in HFM are predefined categories used to organize, categorize, and report financial data efficiently. These dimensions play a pivotal role in structuring financial information and ensuring accurate reporting. Common dimensions in HFM include:
- Value Dimension: Tracks different reporting layers, including local currency, translated currency, and elimination adjustments.
- Entity Dimension: Represents the organizational hierarchy, including legal entities, business units, or departments.
- Scenario Dimension: Helps track financial data across different scenarios, such as actuals, budgets, and forecasts.
- Account Dimension: Categorizes various financial accounts like revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
- Period Dimension: Represents time periods such as months, quarters, and years for financial reporting.
- Value Dimension: Tracks different reporting layers, including local currency, translated currency, and elimination adjustments.
3. Value Dimensions and Currency Translation
HFM's value dimension ensures accurate reporting and financial consolidation across multiple currencies.
- Currency Translation: Value dimensions allow users to manage currency conversions and track different reporting layers, such as local currency, translated currency, and elimination adjustments.
- Consolidation of Multinational Data: Organizations with global operations rely on this feature for consistent and comparable financial reports.
4. Consolidation Process
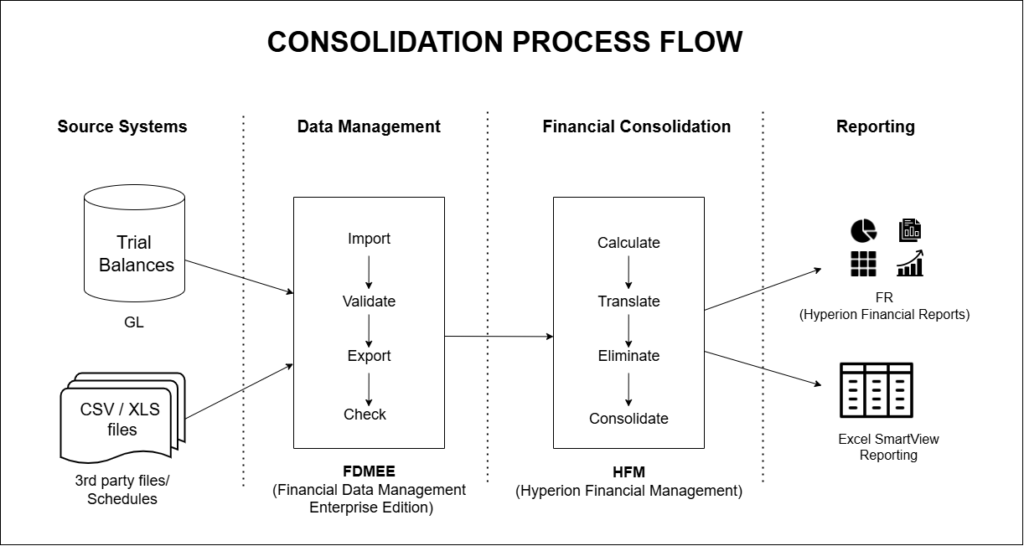
One of HFM's core functionalities is the financial consolidation process.
- This process aggregates financial data from multiple entities into a single, unified report.
- It ensures accurate elimination of intercompany transactions and supports audit trails for financial integrity.
- The consolidation process is automated, reducing manual errors and saving time for finance teams.
5. Intercompany Elimination
Intercompany elimination is the process of removing financial transactions between related entities within the same organization to avoid duplication and ensure accurate consolidated financial reports. Intercompany transactions can distort consolidated financial statements if not handled correctly.
- HFM automates the elimination of these transactions to ensure accurate reporting.
- This functionality is particularly useful for large corporations with multiple internal transactions between subsidiaries.
6. Validation Rules and Calculations
Validation rules and custom calculations are integral to ensuring accurate financial reporting:
- Validation Rules: Defined checks ensure that the data complies with predefined constraints before processing, thus improving data accuracy during consolidation.
- Business Rules for Calculations: These are customizable scripts that automate complex processes such as intercompany eliminations, currency translations, or other financial computations within HFM.
7. Member Lists
Member Lists simplify data organization and reporting within HFM by grouping similar members:
- Purpose: These lists streamline operations by specifying which dimension members (e.g., specific accounts or entities) should be included in a form or report.
- Dynamic Lists: Conditional lists that adapt based on criteria, ensuring flexibility when dealing with evolving business structures.
8. Metadata Management
Proper structuring of metadata ensures that HFM aligns with business reporting needs:
- Definition: Metadata encompasses accounts, entities, scenarios, and custom dimensions essential for financial processes.
- Custom Dimensions: These are tailored dimensions defined by businesses to categorize and track financial data beyond standard categories like time and currency.
9. Consolidation Process in HFM
Consolidation is the method of combining financial data from multiple entities to generate a unified and accurate view of an organization's financial position, including automatic handling of eliminations for intercompany transactions.
The consolidation process is a cornerstone of HFM's functionality:
- Entity Roll-Up: Aggregates financial data from subsidiary entities into a parent entity for a comprehensive view.
- Eliminations: Automatically removes intercompany transactions during consolidation to prevent duplication of revenue or expenses.
10. POV (Point of View) Concept
POV is a contextual filter in HFM that allows users to define the scope for data entry and reporting by selecting key dimensions such as period, entity, and scenario, either dynamically (Selectable POV) or through fixed values (Background POV). POV allows users to control the context for data entry and reporting in HFM:
- Selectable POV: Users can interactively select members (e.g., specific scenarios, periods, or entities) from dropdowns.
- Background POV: Predefined and hidden selections that the user cannot change during form or report access, ensuring consistency in data processing.
Use Cases of HFM

- Global Financial Close and Reporting: Multinational corporations use HFM to consolidate data from multiple entities and report in various currencies.
- Statutory and Management Reporting: Ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks such as IFRS and GAAP while generating internal management reports.
- Intercompany Reconciliation: Simplifies and automates reconciliation between entities to avoid discrepancies.
- Scenario-Based Planning: Companies can evaluate financial performance under different scenarios for better forecasting and decision-making.
- Audit and Compliance: HFM provides an audit trail, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance during financial reporting.
Conclusion
This blog provided an overview of Oracle Hyperion Financial Management (HFM), covering key concepts like data forms, dimensions, consolidation, intercompany eliminations, and reporting tools. These features make HFM essential for enterprises seeking streamlined financial operations and accurate reporting.
Looking ahead, HFM is expected to evolve with enhanced automation, integration with AI-driven analytics, and cloud-native solutions, enabling businesses to gain deeper financial insights and adapt to dynamic market conditions. Check out the official Oracle Hyperion Financial Management website for more details. Also check out our blog on Oracle Hyperion products here!

